Clinical Skills
Discover guidance for assessing patients, diagnostic testing, and surgical procedures through expert-led articles and videos. Perfect for general practitioners, veterinary students, and residents looking to refine their skills.
Test your knowledge on diagnosing, managing, and understanding zoonotic risks of Giardia spp in dogs and cats with this brief clinical quiz.
Topics In Clinical Skills
Featured in Clinical Skills
Poll
Brought to You by Elanco

Quiz
Brought to You by Elanco

New in Clinical Skills
Sponsored byHill's Pet Nutrition
Sponsored byHill's Pet Nutrition
1h:07m:24s
Ep. 357
Sponsored byPRN® Pharmacal
Sponsored byPRN® Pharmacal
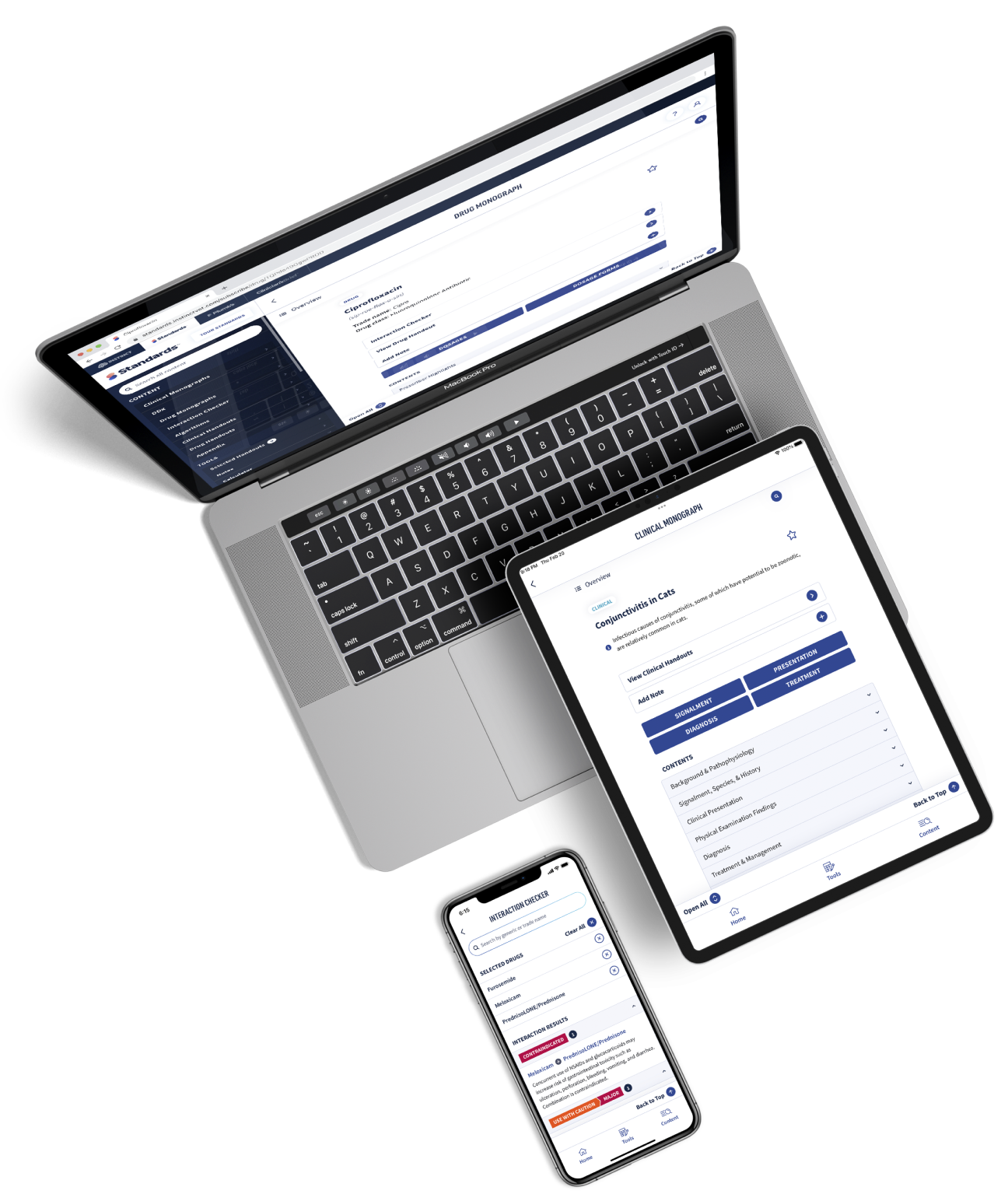
Get more clinical guidance with Standards of Care™
From the team that brings you Clinician’s Brief, extend your knowledge with expert-written, peer-reviewed diagnostic and treatment guidance as well as pet owner education and all the reliable drug information you love in Plumb’s.