Nerve Blocks for Oral Surgery in Cats
Brett Beckman, DVM, FAVD, DAVDC, DAAPM, Animal Emergency Center of Sandy Spring, Atlanta, Georgia; Orlando Veterinary Dentistry, Lake Mary, Florida; Florida Veterinary, Dentistry & Oral Surgery, Punta Gorda, Florida
See the companion article, Nerve Blocks for Oral Surgery in Dogs
Nerve blocks for oral surgical procedures in cats provide a complete sodium channel blockade, preventing ascending pain signals that are created during surgical manipulation to reach the cerebral cortex. Because of their high surface area to body ratio, cats are particularly susceptible to hypothermia. Nerve blocks not only provide perioperative analgesia but allow inhalant anesthetic concentrations to be minimized. Doing so maximizes cardiac output, blood pressure, and overall perfusion, resulting in warmer patients.
Bupivacaine is the anesthetic of choice for oral nerve blocks because of its long duration of action (6–10 hours). Its maximum extravascular dose is determined by patient weight; a safe target maximum dose is 2 mg/kg (Table), but this dose is not commonly reached.
Table: Infusion Volume of 0.5% Bupivacaine per Site Based on Patient Weight
Types of Nerve Blocks
Several types of nerve blocks can be used for oral surgery in cats:
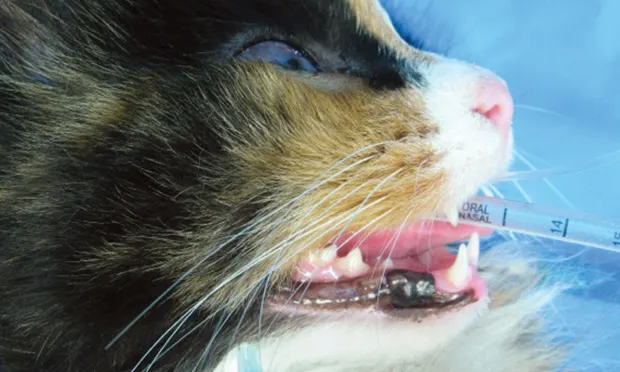
Rostral maxillary (infraorbital) blocks affect the entire maxillary arcade on the ipsilateral side, adjacent bone, tooth, soft tissue, hard and soft palatal mucosa, and palatal bone.
Rostral mandibular (mental) blocks affect bone, teeth, and intraoral soft tissue from the mandibular canine to the mandibular symphysis.
Caudal mandibular (inferior alveolar) blocks affect bone, teeth, and intraoral soft tissue from the mandibular molar rostral to the midline.
Care should be taken not to inject a vessel. Extravascular placement can be ensured by aspirating the needle before injection.
Presurgical Considerations
In small cats, multiple quadrant blocks may approach or exceed the recommended maximum per patient volume of anesthetic agent. It is important to pay careful attention so as not to exceed the total volume. Cats are more susceptible to lidocaine and bupivacaine toxicity than are dogs.
If the volume of agent is less than 0.1 mL per site based on the calculated maximum dose, saline can be added to the agent to dilute it to a ratio of up to 1:1 without compromising the effectiveness of the block.
Some patients chew and/or macerate their tongue following regional oral nerve blocks. Sternal recumbency can prevent lateral deviation of the tongue between the carnassial teeth where damage can occur. As long as the patient is monitored carefully after surgery until it is sternally recumbent, such damage cannot occur.
Related Article: Peripheral Nerve Block Techniques: Dental Blocks
What You Will Need
Tuberculin syringe
25-gauge, 5/8-inch needle
0.5% bupivacaine
Optional: feline skull to visualize anatomic landmarks
Step-by-Step: Rostral Maxillary (Infraorbital) Nerve Block
Step 1
To assist with needle placement, visualize the infraorbital foramen that lies a few millimeters dorsal to the apices of the maxillary third premolar. Note that the infraorbital foramen is larger and more dorsal in cats than in dogs.

Author Insight
Unlike in most dogs, in cats the neurovascular bundle is not readily palpable. As long as the needle is advanced against the bone starting rostral to the third premolar in a rostral-to-caudal direction, it should enter the canal with no resistance.
Step 2
Lift the upper lip dorsally, and advance the needle against the bone in a rostral-to-caudal direction, starting rostral to the third premolar (B) and avoiding the thick lip tissue that contains the neurovascular bundle. Aspirate the needle before injection to confirm that no blood enters the needle hub.
Author Insight
Because of the shortness of the feline infraorbital canal (A), performing the rostral maxillary block desensitizes the entire maxillary arcade on the ipsilateral side, adjacent bone, tooth, soft tissue, hard and soft palatal mucosa, and palatal bone. By placing the needle just within the opening of the infraorbital canal, the agent can reach the infraorbital, pterygopalatine, and major and minor palatine nerves.
The needle should pass into the canal without meeting bony resistance. Once the needle is placed, applying gentle lateral movement will yield resistance within the canal rather than free movement beneath adjacent alveolar mucosa.


Step-by-Step: Rostral Mandibular (Mental) Nerve Block
Step 1
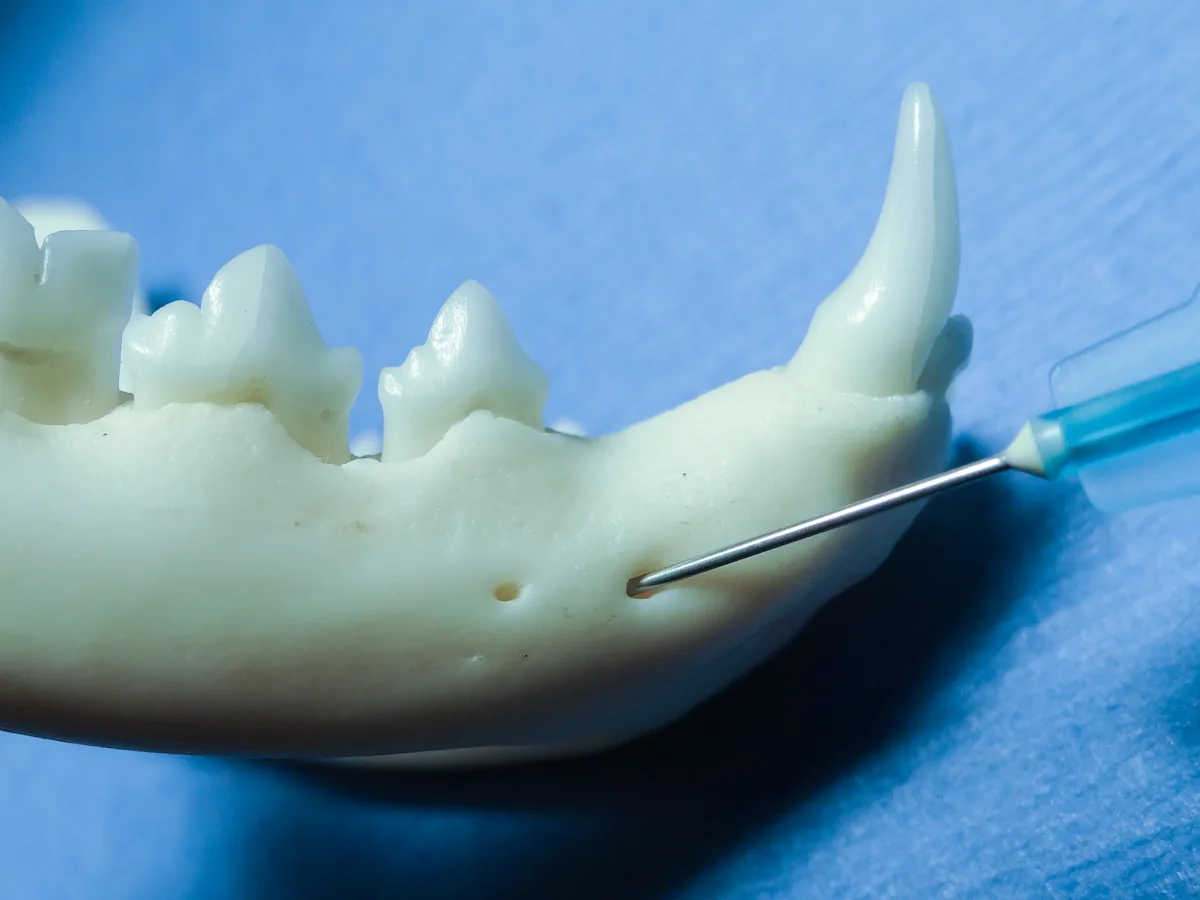
To assist with needle placement, visualize the middle mental foramen, which lies halfway between the mandibular canine tooth and third premolar. The middle mental foramen is one-third to one-fourth the distance from the ventral-to-dorsal mandibular body.
Step 2
Retract the mandibular labial frenulum ventrally, and advance the needle about 15° ventral and caudal to just enter the foramen.
Author Insight
Needle advancement into the canal for the rostral mandibular block may be limited by the size of the cat. The author routinely uses the caudal mandibular block (see below) in cats for this reason.
Step-by-Step: Caudal Mandibular (Inferior Alveolar) Nerve Block
Step 1
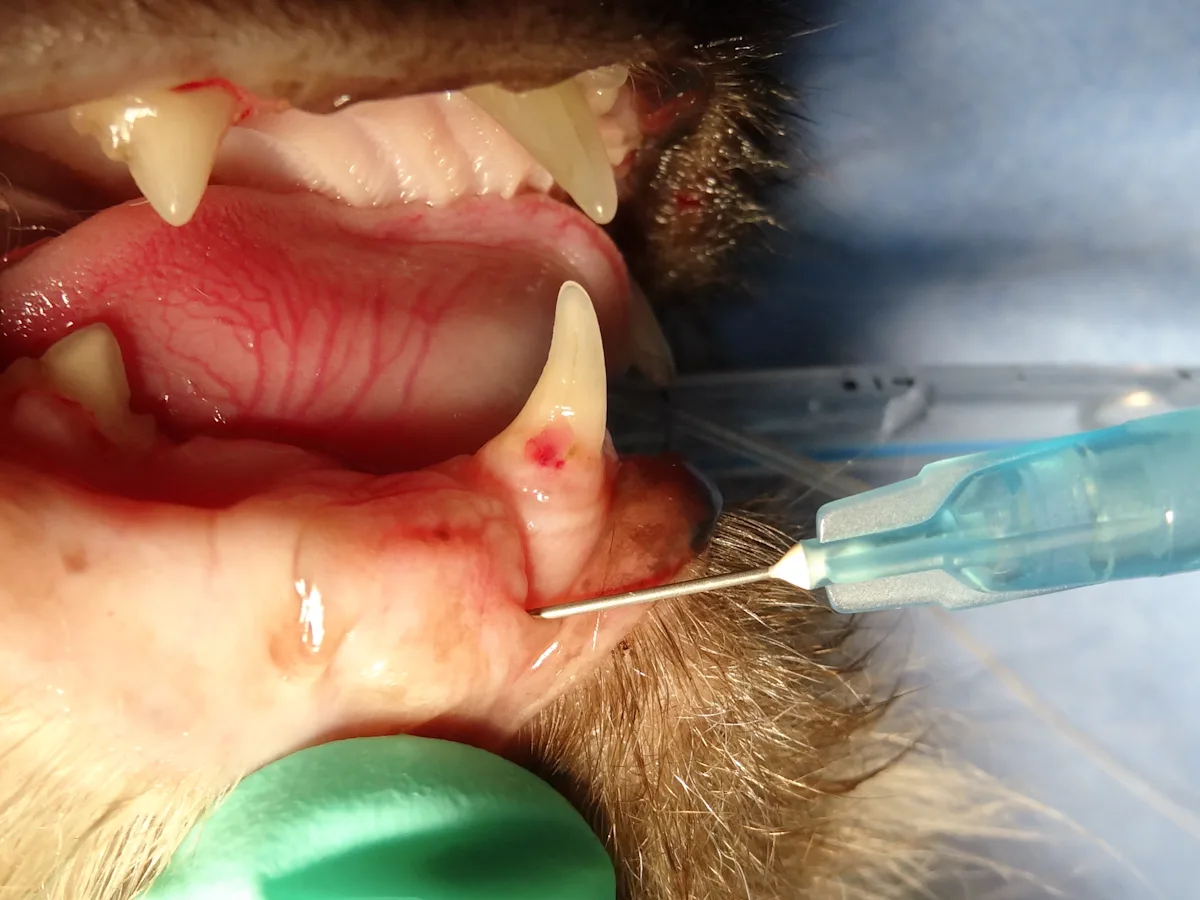
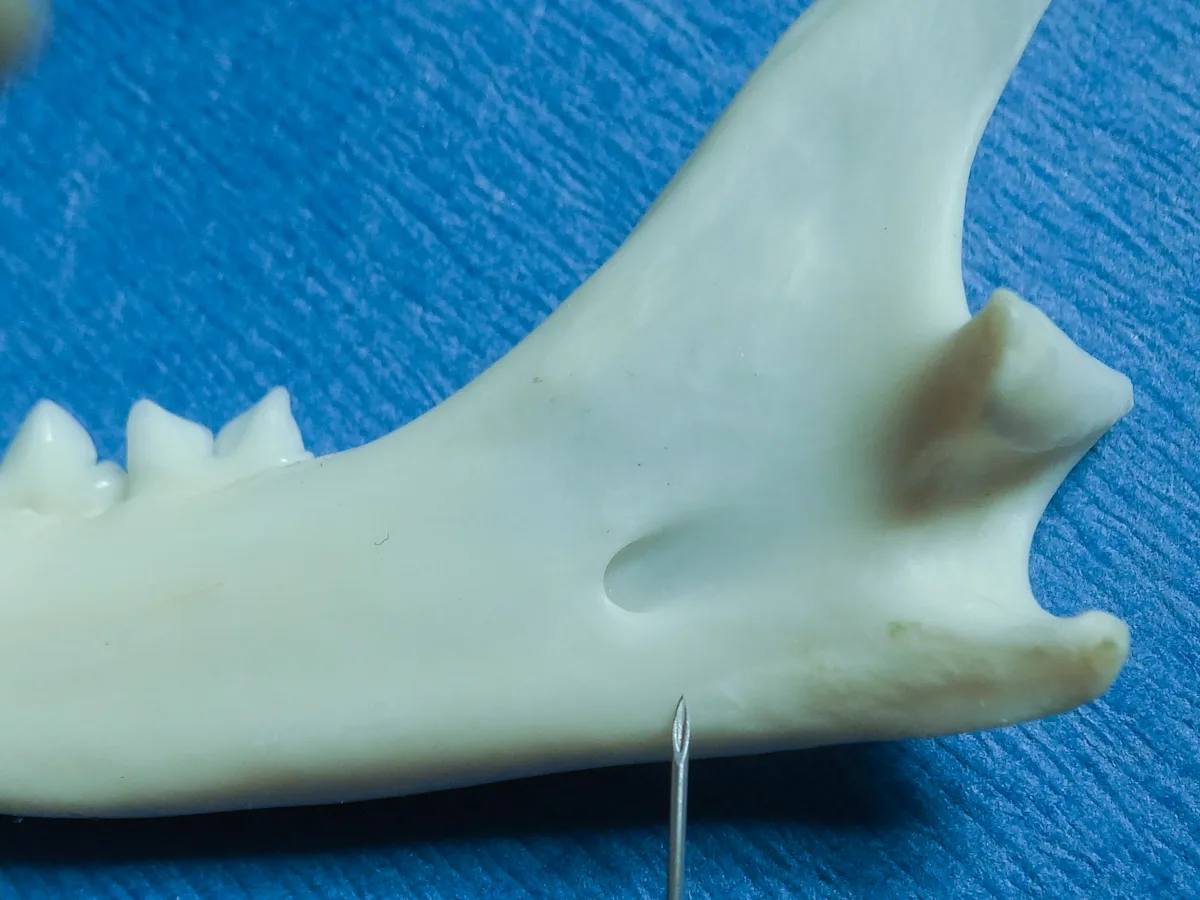
To assist with needle placement for this extraoral block, visualize the lingual and ventral mandibular bone 4–6 mm rostral to the angular process at the caudal mandible (A and B). An alternative landmark is the lateral canthus of the eye. Dropping an imaginary line directly ventral to the ventral mandible allows similar needle placement.

Step 2
Direct the needle through the skin toward the lingual aspect of the mandibular body at an angle of 20°–40°. This allows tactile confirmation that the tip contacts the bone; the needle should be resting just ventral to where the inferior alveolar nerve enters the mandibular canal.
