Variant of Lupus
In this case report, the authors describe a variant of discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) limited to the skin in a 9-year-old Chinese crested dog. The dog had a 9-month history of progressive skin disease characterized by annular to polycyclic, hyperpigmented, scaly to erythematous lesions. Lesions had central whitish macules, papules and plaques, crusts overlying deep erosions/ulcers, or hypopigmented atrophic scars. Except for its skin, the dog was otherwise healthy.
Several 8-mm skin biopsy specimens revealed cell-rich lymphocytic interface dermatitis. Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposition of immunoglobulin (Ig)G, IgM, IgA, and activated complement along the dermal–epidermal junction. The diagnosis was chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE). Systemic lupus erythematosus was ruled out via antinuclear antibody titer, serum biochemistry panel, CBC, and urinalysis. Because the lesions resembled those seen in humans with generalized DLE, treatment with 0.1% topical tacrolimus and oral hydroxychloroquine (HCQ; 5 mg/kg q24h) was initiated as is recommended in humans with DLE. The lesions began to improve within 4 days of starting treatment and remission was induced over the next year, with the exception of 3 disease flares, 2 of which occurred during induction.
Commentary
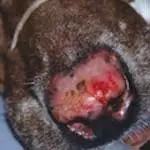
There are 2 interesting features of this skin disease: the description of yet another variant of lupus and the choices for treatment. In this case, lesions did not involve the nose but rather were widespread over the skin. Nasal lesions (Figure 1__Nasal lesions associated with lupus.) of lupus are well recognized, but less so are lesions limited to the skin (Figure 2__. Lesions limited to the skin of a patient with lupus.)
HCQ is an antimalarial drug used in human medicine for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. The drug is contraindicated in patients with preexisting retinal disease, and a complete ocular examination is recommended. HCQ has been used to treat dogs with exfoliative cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ECLE); the disease process was slowed but not cured,1 possibly because ECLE has systemic signs. HCQ as treatment for lupus has been limited in veterinary medicine, but given its low cost and that it is well tolerated, its use may increase.—Karen Moriello, DVM, DACVD
SourceSuccessful treatment of a novel generalized variant of canine discoid lupus erythematosus with oral hydroxychloroquine. Oberkirchner U, Linder KE, Olivry T. VET DERMATOL 23:65-70, 2012.
1. Exfoliative cutaneous lupus erythematosus in German shorthaired pointer dogs:Disease development, progression and evaluation of three immunomodulatory drugs (ciclosporin, hydroxychloroquine, and adalimumab) in a controlled environment. Mauldin EA, Morris DO, Brown DC, Casal ML. Vet Dermatol 21:373-382, 2010.
This capsule is part of the One Health Initiative