Top 5 Mechanisms of Adverse Drug Events in the Intensive Care Unit
Andrew Linklater, DVM, DACVECC, Veterinary Specialists of the Rockies, Castle Rock, Colorado
Drug interactions can occur in the veterinary setting and may result in negative consequences to the patient. A drug interaction refers to a reaction between one or more drugs that alters the effect of or affects the properties of one or both drugs.
Drug interactions can occur during or after administration and may be synergistic, antagonistic, or additive. Interactions between incompatible drugs are always antagonistic. Antagonistic interactions result in decreased drug effectiveness when one drug alters the absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of another or when the interaction causes a direct pharmacodynamic effect 1 that harms the patient. An adverse drug event (ADE) refers to patient injury related to a medical intervention involving a drug.
Critically ill patients are at increased risk for ADEs because they often receive multiple medications concurrently and have serious diseases that may be exacerbated by administration of these medications. The frequency and severity of drug interactions in veterinary intensive care units (ICUs) are unknown, as no standard reporting mechanisms have been established. Reports in human medicine vary substantially: 8.5% to 15% (per 100 admissions) of patients admitted to an ICU may have an ADE,2-4 with up to 54% of patients having a potential drug–drug interaction.5 Adverse events have been associated with a more costly and longer ICU stay.2,4 Most reported ADEs in humans were considered significant or serious, with a smaller percentage being potentially life-threatening or fatal.3,6 Extra-label use of medications, a common practice in veterinary medicine, has been reported to increase ADEs in ICUs.7 Veterinary staff must be diligent in reviewing all medications prescribed to a patient, including reviewing each drug’s dosage, potential adverse effects, and known and potential interactions with other medications.1,8
Drug interactions come in many forms, including:
Incompatibilities of drugs administered at the same time to the same patient
Ineffectiveness of a single drug when a certain carrier or environment (eg, gastric acidity) is present
Dosing errors that move outside the therapeutic dose (likely the most frequent)9-11
Drugs or certain disease processes that alter a drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion
Direct pharmacodynamic interactions
Adverse effects1
This article presents the author’s top 5 potential mechanisms of ADEs in the ICU.
1. Incompatibility
Many drugs are chemically incompatible, often due to the pH or carrier molecules in the drug formulation. For example, diazepam is not compatible with many drugs because of the propylene glycol carrier, enrofloxacin may have decreased availability when administered with divalent cation (calcium or magnesium)-containing solutions, and the injectable forms of butorphanol and furosemide—both often administered to patients presented with respiratory distress from congestive heart failure—may form a precipitate if administered together.
Butorphanol (for sedation) and furosemide (a potent loop diuretic) are common initial treatment choices for patients presented with acute congestive heart failure. Both injectable medications can be given intravenously or intramuscularly, but they cannot be combined. Furosemide is a mildly alkaline, buffered product and should not be mixed with solutions that have a pH less than 5.5; the pH of butorphanol varies between manufacturers but may be between 3.0 and 5.5.8,12,13 When these drugs are allowed to interact through combination in a syringe or an IV line, a cloudy precipitate may form (Figure 1, above). This precipitate can damage tissue or occlude a vessel—particularly in the cerebral and pulmonary vasculature, which can be life-threatening—and one or both drugs may be ineffective. To prevent this interaction, drug compatibility should always be determined prior to combination (in a syringe) or coadministration of drugs in any fluid lines; in addition, the fluid line should be thoroughly flushed with a compatible solution between administration of each drug.
2. Related Mechanisms of Action & Additive Effect
Critically ill patients are susceptible to GI ulceration (Figure 2) because of many factors, including primary or secondary GI disease, surgery, hypoperfusion, and mechanical ventilation. These patients also often require corticosteroids or NSAIDs because of inflammation, pain, and adrenal or immune-mediated disease. Ulceration can result in GI dysfunction, hemorrhage, and/or perforation.
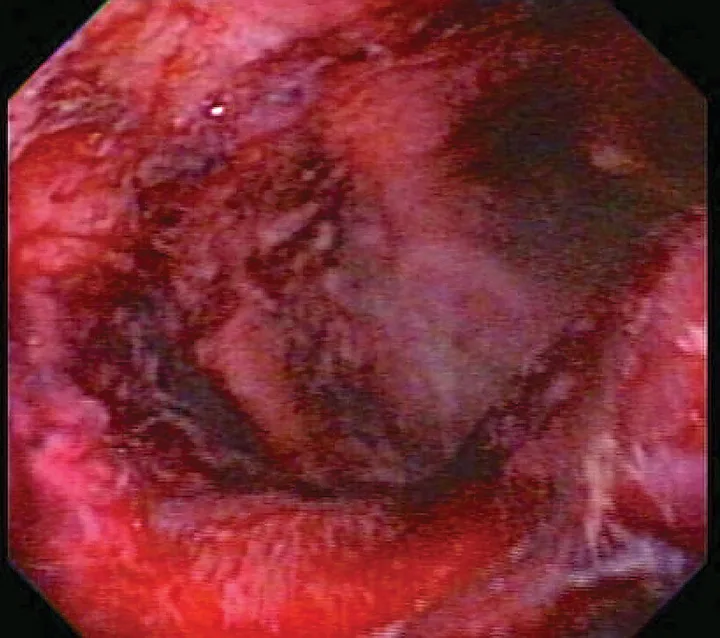
Endoscopic image of duodenal ulcers in a critically ill patient
Corticosteroids and NSAIDs typically should not be used together, as their combined actions are likely to cause severe GI ulceration. Corticosteroids exert their anti-inflammatory effect in part through inhibition of several enzymes in the arachidonic acid cascade (eg, phospholipase A2, cyclooxygenase); NSAIDs also inhibit cyclooxygenases.14 The arachidonic acid cascade is important for maintaining normal GI mucosa and renal perfusion. Inhibition of prostaglandin production results in poor GI blood flow and poor mucosal barrier function, exposing the mucosa to the low pH of gastric acid and causing development (and poor healing) of gastric and intestinal ulcers.15,16
When a patient requires a change in anti-inflammatory medication, a “washout” period between medications should be observed. The ideal washout period has not been established for all drugs, but a period of 4 to 5 half-lives of the individual drug (resulting in a time frame of 3-5 days for many drugs) has been suggested anecdotally.17-19 When a washout period is not possible, a patient has inadvertently been administered more than one anti-inflammatory drug, an overdose is suspected, or a patient is known or suspected to have GI ulceration, gastroprotective medications should be started, and the anti-inflammatory drug should be discontinued, if possible. Medications that may treat or prevent gastric ulcer formation include H2-receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, sucralfate, or prostaglandin analogues.20 Although proton pump inhibitors are more effective as acid reducers than are H2-receptor antagonists, their onset of action may be prolonged.
3. Inhibition of Absorption
GI ulceration is common in critically ill patients and can cause protein and blood loss, poor appetite, pain, poor nutrition, vomiting, and sepsis. Sucralfate is a sucrose–sulfate–aluminum complex that in the acidic environment of the stomach is converted into a paste to provide a physical barrier over an ulcer. It adsorbs pepsin and bile acids, prevents diffusion of hydrogen ions into the gastric mucosa, and may stimulate the production of prostaglandin E,21 all of which promote an environment for GI ulcers to heal.
Sucralfate interferes with the absorption of many drugs, such as antibiotics and antifungal drugs.22-24 Because it has the potential to decrease absorption and the effectiveness of other orally administered medications,21,25-27 sucralfate should be administered at least 2 hours before or after other oral medications. This separation has resulted in improved absorption of some drugs; however, ideal time frames for all drugs have not been determined.
4. Neurologic Side Effects
Many ICU patients may have either an existing primary neurologic disease or have a condition that secondarily affects the neurologic system (eg, hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, hypernatremia). In addition, ICU patients are commonly exposed to a variety of medications that can affect the neurologic system, such as analgesics (eg, opioids, tramadol), prokinetic medications (eg, metoclopramide), antibiotics (eg, metronidazole), and sedatives (eg, acepromazine, trazodone, benzodiazepines, α2 agonists).
Trazodone and tramadol are commonly used drugs for which use has increased substantially in the last several years. Trazodone is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor and has several reported mechanisms of action.28 When combined, these drugs can cause serotonin syndrome (Figure 3), a condition characterized by GI signs (eg, vomiting, diarrhea), cardiorespiratory signs (eg, dyspnea, arrhythmias), and neurologic signs (eg, seizures, hyperthermia, hyperesthesia, depression, vocalization, ataxia, coma). Although serotonin syndrome has not been reported with coadministration of trazodone and tramadol in animals, it has been observed in humans when both trazodone and tramadol are used in combination with opioids and other serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors—occasionally with lethal consequences.29-31
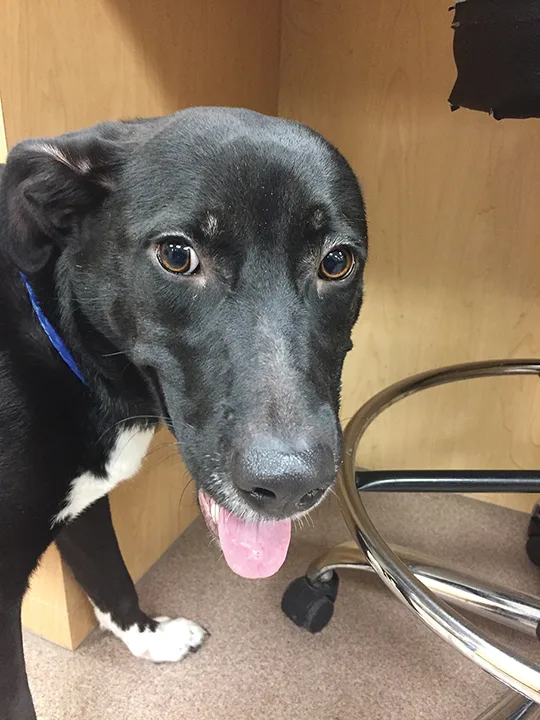

Patient with serotonin syndrome with tachypnea, tachycardia, mydriasis, and agitation
Any medications with a similar mechanism of action should be prescribed together cautiously; if adverse effects are noted, both drugs should be discontinued and appropriate supportive care initiated.
5. Effects on Potassium
ICU patients often require treatment for conditions that affect serum potassium concentration, including urinary tract disease, toxicities, diabetes, adrenal gland disease, abdominal effusions, and nutritional deficiencies. Potassium concentration should be monitored closely in these patients, as severe hyperkalemia can lead to altered cardiac function and death (Figure 4), and severe hypokalemia can cause muscle weakness, poor GI function, hypoventilation, and death.
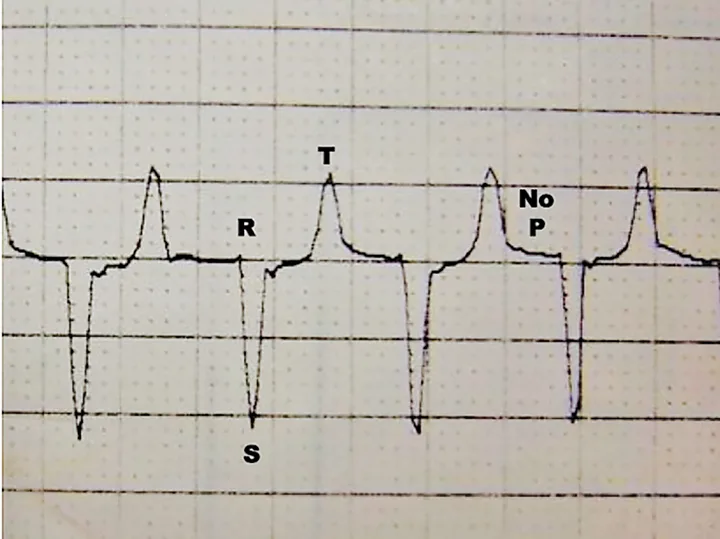
ECG from a cat with hyperkalemia caused by urethral obstruction. Atrial standstill (absent P waves) can be seen with supraventricular escape beats at 140 bpm.
Many drugs can alter potassium levels and exacerbate many of these conditions. Hyperkalemia can occur after administration of potassium-containing fluids, potassium supplementation (eg, potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, potassium acetate), NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors, and spironolactone. Hypokalemia may occur following administration of IV fluids, insulin, sodium bicarbonate, dextrose, diuretics, and β agonists (eg, epinephrine, terbutaline). Any patient that is hospitalized and receiving any of these medications, particularly if any of the conditions noted in this article are present, should have serum potassium concentration monitored closely and corrected if necessary.
ADE = adverse drug event, ICU = intensive care unit