Animals are frequently presented with the chief complaint of having a "red eye." Redness typically represents inflammation of the ocular tissues, which may be a normal variant or require topical therapy or emergency surgery.
Inflammation or infection can occur with diseases of the external eyelids, nictitans, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, orbit, or intraocular structures (uvea, choroid). Inflammation is often accompanied by hyperemia of the lids or conjunctiva, blepharospasm, increased blinking, rubbing of the eye, epiphora, or excessive discharge. Additionally, clouding of ocular structures, altered intraocular pressure, and decreased vision or blindness can be seen.
Related Article: Conjunctival Samples in Dogs & Cats
Meticulous examination of the eye with a methodical diagnostic approach will aid in obtaining an accurate diagnosis and help determine treatment. Dimming room lights is imperative before performing the ocular exam. A complete ophthalmic exam uses a focal light source to examine the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior surface of the iris. Direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy may be performed by using a short-acting agent such as tropicamide to examine the posterior segment. In conjunction with the ocular exam, Schirmer's tear testing, fluorescein staining, and tonometry should be performed in every patient.
Cytology may be useful for conjunctival or corneal scrapings. A mini-tip culturette may be needed to obtain bacterial cultures. Blood assays (CBC, chemistry profile, tick serology, fungal serology) and blood pressure measurements may be necessary to complete the workup and should also be employed if systemic disease is suspected.
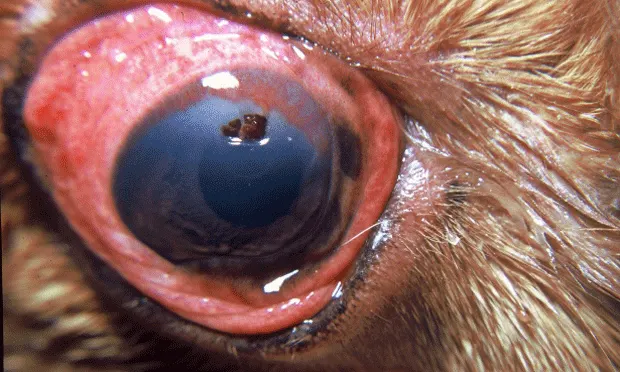
The following photographs illustrate numerous clinical presentations of "red eye."
Related Article: Image Gallery: Cataracts

8-year-old wire fox terrier—Acute glaucoma
This dog presented with acute ocular pain of 3 days, blepharospasm, conjunctival hyperemia, diffuse corneal edema, and reduced vision. Applanation tonometry revealed an intraocular pressure of 55 mm Hg. Emergency glaucoma therapy was indicated.