Quiz: Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases in Dogs
Jonathan Dear, DVM, MAS, DACVIM (SAIM), University of California, Davis
Recognizing infectious diseases can be challenging, as clinical signs and laboratory findings are often similar among diseases and may mimic neoplastic or immune-mediated disease. The cases presented here illustrate how some uncommon but re-emerging infectious diseases can be identified rapidly and treated appropriately.
Case 1
A 3-year-old, neutered male crossbreed sighthound is presented with a week-long history of lethargy and progressive loss of appetite. The dog was recently adopted from a shelter in the Los Angeles area and appeared healthy at adoption. He received all core vaccinations and was neutered while under the care of the shelter.
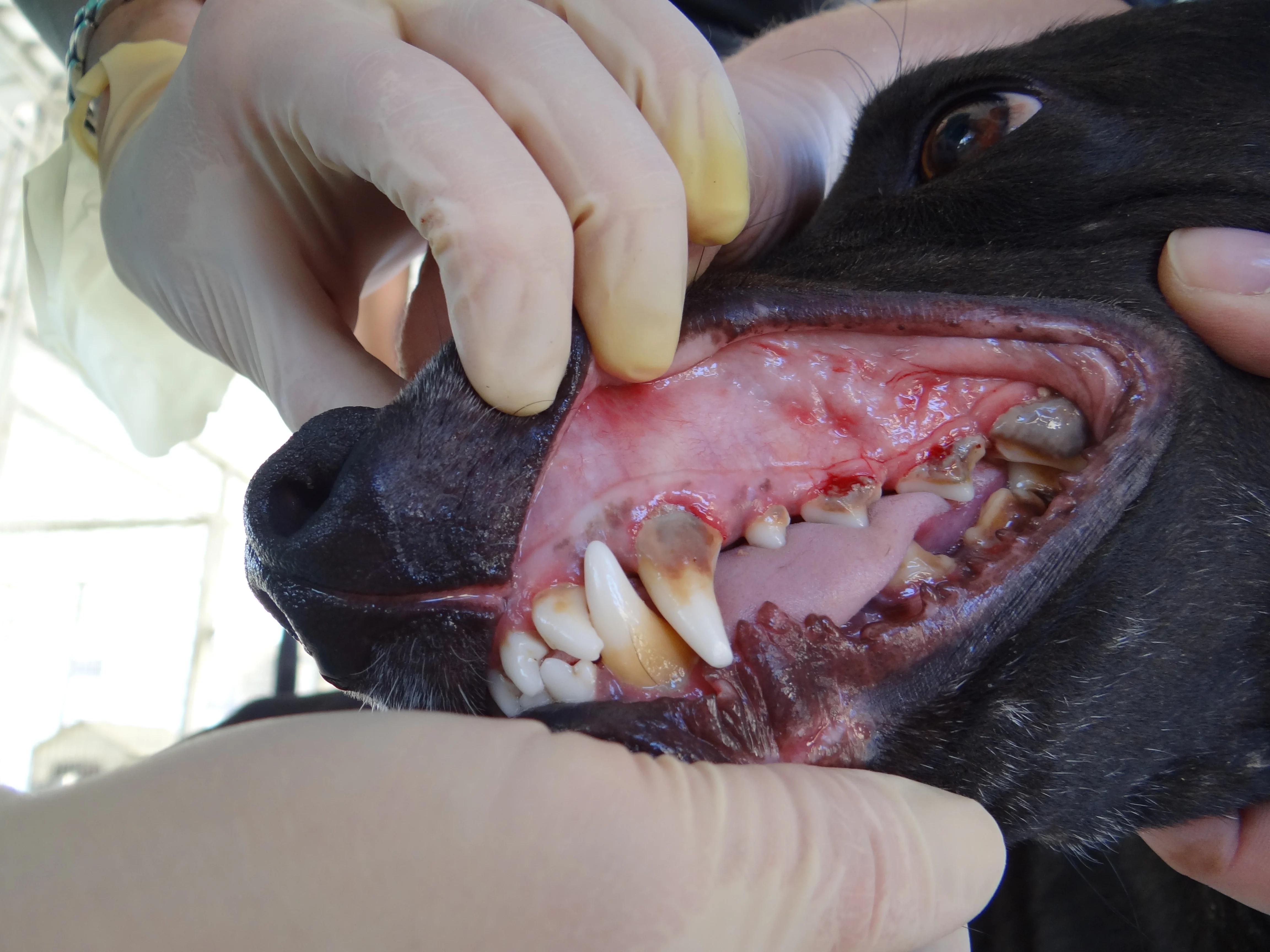
On physical examination, the veterinarian notices pale mucous membranes with pinpoint petechiae (Figure 1). Abdominal palpation reveals moderate splenomegaly. The remainder of the examination is within normal limits.

CBC results reveal normal values for lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. However, the following parameters are outside reference ranges:
MCHC = mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, MCV = mean corpuscular volume, MPV = mean platelet volume
Case 2
A 4-year-old spayed German shepherd dog is presented to an emergency clinic for acute onset of paraparesis. On physical examination, the dog has an elevated temperature (103.2°F [39.6°C], normal 100°F-102.5°F (37.8°C-39.2°C), along with apparent pain on palpation of the thoracolumbar spine. Neurologic examination reveals a quiet dog with all appearances of appropriate mentation. All cranial nerves appear within normal limits, but the dog has delayed postural reactions bilaterally with increased segmental reflexes in the pelvic limbs. The thoracic limbs appear unaffected. Fundic examination reveals an ill-defined area of hyporeflectivity in the tapetum.