Profile
Definitions
Overweight dogs are 10% to 20% above ideal body weight.1
Obese dogs are > 20% above ideal body weight.
Resting energy requirement is the energy requirement for a normal but fed animal at rest in a thermoneutral environment.2
Maintenance energy requirement is the energy requirement of a moderately active adult animal in a thermoneutral environment.
Malnutrition is any disorder of nutrition with inadequate or unbalanced nutrition.3
Includes both nutrient deficiencies and nutrient excesses.
Most common cause in dogs is overnutrition or excessive intake of nutrients.
Weight rebound is the propensity to regain weight after a successful weight loss program due to adaptive downregulation of resting energy requirement.4
Dietary thermogenesis (also called specific dynamic action of food) refers to the energy needed by the body to digest, absorb, and assimilate nutrients.5
Incidence/Prevalence
Obesity is the most common nutritional disorder seen in dogs.
An estimated 25% to 44% of dogs in the United States are overweight or obese.
Genetic Implications
Genes associated with obesity have been found in humans and rodents but not dogs; however, because certain breeds are at greater risk for obesity than others, there is probably a genetic component to obesity in some dogs.
Signalment1,6
Certain breeds of dogs are predisposed to obesity, including Labrador retriever, dachshund, sheltie, cocker spaniel, beagle, basset hound, Cavalier King Charles spaniel, and cairn terrier dogs. The incidence of obesity in dogs increases after 2 years of age and plateaus at about 6 to 8 years of age.
Obesity is more common in females than males.
CausesImbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure: intake exceeds expenditure.
Risk Factors
Overeating: due to internal and external factors; external factors include
Availability and improved palatability of pet foods
Competition for food from other animals present at the time of feeding
Begging at the table
Receiving high-fat treats
Lack of exercise: parallels trend in humans.
Breed: certain breeds are at greater risk (see breed predilection section above).
Age
Aging is associated with a decrease in lean body mass and metabolic rate.
Aging is often associated with medical conditions, such as degenerative joint disease, that interfere with the ability to exercise.
Middle-aged and older dogs tend to be less active than very young dogs.
Neutering: gonadectomy increases the frequency of obesity in males and females.
Endocrine disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperadrenocorticism (It is important that the pot-bellied appearance of some dogs with hyperadrenocorticism not be misdiagnosed as obesity.)
Drugs that increase appetite, such as corticosteroids and phenobarbital.
Pathophysiology
There are two types of obesity identified in humans and rodents and which probably occur in dogs;6 the age at which obesity first occurs determines the type:
Hypertrophic obesity is characterized by enlargement of fat cell size. It is generally seen with adult onset of obesity. Overfeeding during adulthood increases the size but not the number of fat cells.
Hyperplastic obesity is characterized by an increase in both size and number of fat cells. It is generally seen with onset of obesity during growth and puberty.
Once fat cells develop, they usually do not disappear, even with successful weight loss, but rather remain as a stimulus to regain weight.
Pets with this type of obesity are generally more difficult to treat and have a poorer long-term prognosis.
Health risks associated with obesity in dogs; the term "epidemic" is being applied to the high prevalence of obesity in humans and their pets.
Conditions caused or complicated by obesity:
Decreased life expectancy7 (A longevity study in dogs showed that obese dogs have a 2-year decrease in life expectancy compared with nonobese paired littermates.)
Increased incidence of hip dysplasia and degenerative joint disease7-10
Pulmonary and cardiovascular disease11,12
Reduced immunity13
Exercise and heat intolerance14,15
Hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia
Increased incidence of pancreatitis16
Dystocia and possibly decreased fertility
Hypertension17-19
Increased incidence of mammary tumors and transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder20
Diabetes mellitus
Malassezia dermatitis and skinfold dermatitis
Difficulty with performing surgical procedures
Increased morbidity and mortality during and after anesthesia (Many anesthetics are fat-soluble, so obese animals may take longer to recover from anesthesia; complications associated with ventilation during anesthetic procedure may occur.)
Diagnosis
History
Histories may vary, but owners often report that the dog is lethargic, cannot tolerate exercise or heat, or has orthopedic problems.
Physical Examination
Routine physical examination should include body weight and a body condition score (BCS); body weight recorded without being correlated with some kind of index of body condition is often difficult to interpret.
BCS is a subjective assessment of body fat and, to lesser extent, protein stores.13
Is accurate when used by properly trained individuals.
Two BCS scales can be used. See Tables 1 and 2.
Treatment
Step 1-Acknowledge that obesity is present.
On physical examinations, veterinarians often note BCSs that are consistent with obesity, yet fail to acknowledge obesity as a problem.21
Step 2-Obtain a thorough diet history from the owner.
Interviewing client about what and how the pet is fed provides important information about caloric intake and sources of calories.
It also helps identify potential problems in advance (eg, multipet households, indulgent owners, beggars).
Step 3-Form a partnership with the owner.
Short- and long-term success of a weight loss program largely depends on the client's accepting the need for weight loss and doing his or her part to achieve success.
Clients must understand the risk factors of obesity.
Clients must feel good about the lifestyle changes needed to address obesity and prevent its recurrence.
Step 4-Correct or control any underlying diseases.
Rule out endocrine disorders and appropriately treat any diseases diagnosed.
Step 5-Induce a negative energy balance.
The most effective way to induce a negative energy balance is to combine energy restriction with exercise, an all too often forgotten component of a weight loss program.
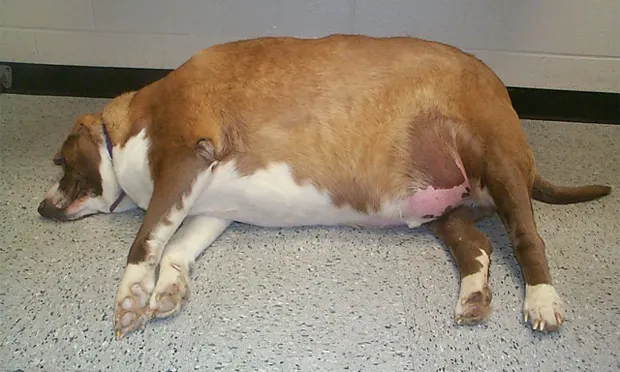
The severity of obesity or concurrent orthopedic problems in some dogs prevents them from safely going on walks (Figures 1 and 2).
Consider enrolling these patients in an underwater treadmill exercise program to decrease weight so the owners can walk them at home.
These programs allow low-impact exercise and are well tolerated by even the most obese dogs (Figures 3 and 4).

Figure 1. A 4-year-old castrated male springer spaniel mix that weighed 187 pounds. The dog had repeated work-ups for endocrine disorders; none was ever found. The dog spent most of his time in lateral recumbency. He had great difficulty standing and could stand for only brief periods. The owner could not walk the dog because of its morbid obesity.

Figure 2. Another view of the 4-year-old castrated male springer spaniel mix that weighed 187 punds. The dog is wider than the scale used to weight it.

Figure 3. The same dog as in Figures 1 and 2 six months after starting an obesity management program (commercial diet formulated for weight loss and underwater treadmill exercise sessions 3 times a week). The dog’s weight had decreased to 137 pounds, and his quality of life was dramatically improved. In addition to the underwater treadmill exercise sessions, the owner could now take the dog on short walks at home.

Figure 4. The same dog as in Figures 1 through 3 after losing 71 pounds (weight 116). After losing 50 pounds, the dog’s attitude and energy level were dramatically improved. The treadmill sessions were eventually discontinued, and the dog’s weight loss program was modified to include 0.5-mile walks every day by the owner. The therapeutic weight loss diet was continued.
Step 6-Calculate caloric requirements. (See Obesity Management Calculation Sheet)
Initial caloric calculations are only starting points; they may need to be modified according to the dog's individual response.
Should you use "ideal" or "current" body weight in your calculations? Both methods have shown success. Advantages of using "current" body weight include the following:
Takes the guesswork out of determining "ideal" body weight for each patient.
Less chance of immediately restricting caloric intake to a level that downregulates thyroid hormone production and results in downregulation of metabolic rate.4
Reduces the likelihood of "weight rebound" after successful weight loss;4 rebound is more likely when severe caloric restriction is used during the weight loss program.
In very obese patients, an exception to using "current" body weight in your calculations for caloric intake may need to be taken. Fat does not contribute significantly to metabolic rate; therefore, caloric requirements can be overestimated in very obese patients. In these patients, underestimate how much weight the patient should lose to reach an ideal body weight so that you do not adversely affect the metabolic rate.
Step 7-Choose an appropriate diet for weight loss.
Most pet food companies that make therapeutic diets foods that can be used in a weight loss program; these diets provide reduced calories and adequate levels of all nutrients.
Avoid using a standard maintenance diet for a weight loss program.
Such diets are formulated to meet the nutritional needs of pets consuming "reasonable quantities" of food; they are not formulated for weight loss.
By restricting caloric intake using a standard maintenance diet, all the other nutrients are also restricted; standard maintenance diets are not formulated for this purpose.
The volume of food will be very small and may lead the dog to beg for food.
Avoid starvation diets.
Starvation restricts not just calories but also every nutrient. Dogs, like humans, have daily requirements for certain nutrients, and starvation fails to provide these nutrients.
Starvation results in loss of more lean body tissue than does reduced caloric intake.
Starvation decreases intestinal mass and surface area and increases the risk for infection and absorption problems.
Outcomes from starvation weight loss programs versus restricted caloric intake programs reveal that the net weight loss with starvation is roughly equivalent to that with restricted caloric intake, but it comes at a much higher cost to the patient.
Starvation during a weight loss program adversely affects metabolic rate and predisposes the animal to weight rebound once the weight loss program is completed.
Starvation is perceived as inhumane by most clients (and veterinarians), and destroys the partnership between the client and the veterinarian that is needed for successful weight loss; if clients do not feel good about the weight loss program for the dog, they will probably refuse to participate in one or discontinue it prematurely.
Step 8-Divide total daily caloric intake into 2 meals.
Meal size and frequency influence postprandial thermogenesis in dogs22 (thermogenesis is increased by feeding multiple small meals rather than 1 large meal [ie, it takes calories to digest food]).
Two smaller meals may provide better satiety than 1 large meal.
Step 9-Allow treats to be given if this is part of the human-animal bond that the owner and dog have.
Provide alternative low-calorie treat options (therapeutic weight loss biscuits, canned green beans, carrots and celery sticks, rice cakes, the pet's own weight loss diet).
Limit the amount of treats the owners can give to the dog to < 10% of the dog's total caloric intake (most treats are not complete and balanced; if treats make up too much of the animal's diet, nutrient imbalances may occur).
Step 10-Decide on the rate of weight loss.
Because of the lack of "uniform" sizes of dogs, it is better to recommend a percentage loss of body weight per week than a standard generic quantity for all patients; a weight loss rate of 1% of body weight per week is safe.
Step 11-Weigh the dog at least once every 2 weeks.
This schedule allows early detection of weight loss that is occurring too slowly or has plateaued; if weight loss has plateaued, consider increasing exercise or recalculating caloric intake using the dog's newer and leaner body weight.
It is often difficult to appreciate weight loss in a dog the owner sees every day; biweekly weigh-ins allow clients to appreciate the amount of weight the dog is losing and allows the veterinarian to give positive feedback to and celebrate success with the client.
Step 12-Consider medical therapy for animals that do not respond to traditional methods of management, such as caloric restriction and increased exercise.
Dirlotapide (Slentrol, Pfizer Animal Health; www.pfizerah.com) has recently been approved by the FDA for management of canine obesity. It is an additional tool to assist with effective and reliable weight loss.
Dirlotapide is a selective microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) inhibitor that blocks the assembly and release of some of the lipoproteins from enterocytes into the bloodstream.
Microsomal transfer proteins are found in the intestines and the liver; in vitro studies show that dirlotapide selectively inhibits MTP in intestinal cells.
Dirlotapide does not completely block the release of all triglycerides into the bloodstream. Some triglycerides get trapped in enterocytes and end up in the feces when cells are sloughed.
Dirlotapide works primarily by decreasing food intake. Acting locally in the small intestine to decrease lipid absorption, dirlotapide increases levels of chemical mediators such as neuropeptides PYY and GLP-1 in dogs.
Dirlotapide is not a pancreatic enzyme inhibitor and therefore does not interfere with fat digestion in the gastrointestinal tract. Fat is broken down normally in the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes normal absorption into the enterocytes. Thus, the drug does not cause problems associated with pancreatic enzyme inhibitors (undigested fat passed through the gastrointestinal tract as oily anal discharge).
85% to 90% of dirlotapide's effect in promoting weight loss is due to a reduction in food intake; the remaining 10% to 15% of the effect is due to loss of fat trapped in enterocytes.
Dirlotapide is administered orally Q 24 H.
The most commonly reported side effects with dirlotapide are vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy. Mild to moderate elevations in hepatic transaminases (ALT/AST) that return to normal after the discontinuation of drug therapy have been observed in dogs treated with dirlotapide.
Dirlotapide is contraindicated in cats, as well as in dogs with liver disease or dogs receiving long-term corticosteroid therapy.
The safe use of dirlotapide has been studied for one year.
Dirlotapide does not promote weight loss in every dog. Weight rebound is a problem in some patients once therapy is stopped. Successful long-term management of weight loss requires ongoing management in the form of caloric restriction and exercise after dirlotapide therapy has been completed.
Relative cost of weight loss program
Cost varies depending on the size of the dog.
Yearly cost of therapeutic weight loss diets is generally less than that of repairing a ruptured cruciate ligament in an obese dog.
Underwater treadmill programs are becoming more popular in referral practices and institutions. Many sites will have a weekly rates for multiple sessions.
TX at a glance
Restrict calories using diet formulated for weight loss
Prescribe program of regular exercise
Calculate treats, as indicated by client, as part of overall caloric intake
Consider dirlotapide for obese dogs that do not respond adequately to above
OBESITY MANAGEMENT IN DOGS • Sherry Lynn Sanderson
References1. Obesity. Burkholder WJ, Toll PW. In Hand MS, Thatcher CD, Remillard RL, Roudebush P (eds): Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 4th ed-Marceline, Missouri: Walsworth, 2000, pp 401-430.2. Nutrients. Gross KL, Wedekind KJ, Cowell CS, et al. In Hand MS, Thatcher CD, Remillard RL, Roudebush P (eds): Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 4th ed-Marceline, Missouri: Walsworth, 2000, pp 21-107.3. Small animal clinical nutrition: An interative process. Thatcher CD, Hand MS, Remillard RL. In Hand MS, Thatcher CD, Remillard RL, Roudebush P (eds): Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 4th ed-Marceline, Missouri: Walsworth, 2000, pp 1-19.4. The effect of weight loss regimen on subsequent weight maintenance in dogs. Laflamme DP, Kuhlman G. Nutr Res 15:1019-1028, 1995.5. Energy and water. In Case LP, Carey DP, Hirakawa DA, Daristotle L (eds): Canine and Feline Nutrition, 2nd ed-St. Louis: Mosby, 2000, pp 3-14.6. Obesity. In Case LP, Carey DP, Hirakawa DA, Daristotle L (eds): Canine and Feline Nutrition, 2nd ed-St. Louis: Mosby, 2000, pp 303-330.7. Effects of diet restriction on life span and age-related changes in dogs. Kealy RD, Lawler DF, Ballam JM, et al. JAVMA 220:1315-1320, 2002.8. Effects of limited food consumption on the incidence of hip dysplasia in growing dogs. Kealy RD, Olsson S-E, Monti KL, et al. JAVMA 201:857-863, 1992.9. Five-year longitudinal study on limited food consumption and development of osteoarthritis in coxofemoral joints of dogs. Kealy RD, Lawler DF, Ballam JM, et al. JAVMA 210:222-225, 1997.10. Evaluation of the effect of limited food consumption on radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis in dogs. Kealy RD, Lawler DF, Ballamn JM, et al. JAVMA 217:1678-1680, 2000.11. The medical implications of canine obesity and their relevance to anesthesia. Clutton RE. Brit Vet J 144:21-28, 1988.12. Obesity: Occurrence, treatment and prevention. Hand MS, Armstrong PJ, Allen TA. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 19:447-474, 1989.13. Overnutrition in resistance of dogs to distemper virus. Newberne PM. Fed Proc 25:1701, 1966.14. Management of obesity in the dog. Edney ATB. Vet Med Small Anim Pract 69:46-49, 1974.15. The obese dog and some clinical repercussions. Joshua JO. J Small Anim Pract 11:601-606, 1970.16. Evaluation of risk factors for fatal acute pancreatitis in dogs. Hess RS, Kass PH, Shofer FS, et al. JAVMA 214:46-51, 1999.17. Obesity-induced hypertension in the dog. Rocchini AP. Hypertension 9:64-68, 1987.18. Pathogenesis of weight-related changes in blood pressure in dogs. Rocchini AP, Moorehead CP, DeRemer S, et al. Hypertension 13:922-928, 1991.19. Insulin resistance and blood pressure regulation in obese and nonobese subjects. Rocchini AP. Hypertension 17:837-842, 1991.20. Epidemiologic study of insecticide exposure, obesity, and risk of bladder cancer in household dogs. Glickman LT, Schofer FS, McKee LJ, et al. J Toxicol Environ Health 28:407-414, 1989.21. Health status and population characteristics of dogs and cats examined at private veterinary practices in the United States. Lund EM, Armstrong PJ, Kirk CA, et al. JAVMA 214:1336-1341, 1999.22. Effect of meal size and frequency on postprandial thermogenesis in dogs. LeBlanc J, Diamond P. Am J Physiol 250:E144-E147, 1986.