Imaging Intestinal Obstruction
Linda Lang, DVM, Washington State University
John Mattoon, DVM, DACVR, Washington State University
Jennifer White, BVSc, Washington State University
Small intestinal obstruction from foreign material, masses, and intussusceptions is a common cause of vomiting.1 Recognizing radiographic and ultrasonographic signs is necessary for correct diagnosis.2,3
A backup of ingesta proximal to the obstruction site can cause bowel distention (See Figures 2–6, below). Complete and some chronic partial obstructions can cause significant bowel dilation, and often the colon is empty. Depending on the obstruction site, the segment of bowel distention may be short or long. Compared with the small intestine, the colon is typically larger in diameter and contains fecal material. Differentiating small intestine from colon is crucial for accurate diagnosis: mistaking colon for small intestine can lead to incorrect diagnosis of small bowel obstruction, while mistaking distended small intestine for colon can lead to a missed diagnosis of small intestinal obstruction (Figure 6, below). Both lateral and ventrodorsal views are essential for accurate assessment, although both may not be presented in this collection.
Ultrasonography is often used to assess vomiting and can reliably diagnose small bowel obstruction.4-6 Compared with radiography, ultrasonography can identify underlying causes more frequently.4-6 Challenges include the presence of bowel gas (hiding foreign material), ultrasonographer experience, relatively small field of vision, and differentiation of small intestine from colon.
Overlap exists between normal (See Figure 1) and obstructive bowel diameter.4 Proximal obstructions can have a short segment of duodenal distention, and distal obstructions can have longer segments of small intestinal distention. Recognizing mixed populations of normal and distended bowel is common in small intestinal obstruction. The small intestine should contain only homogeneous soft tissue opacity (fluid, liquid ingesta) and/or gas. Heterogeneous material (often feces-like) is a sign of potential obstruction from foreign material or inhibition of passage of normal ingesta.
1. Normal Small Intestinal Diameter, Contents, & Distribution

In dogs, a ratio of 1.6:1 for small intestinal diameter (white arrows) relative to height of fifth lumbar (L5) vertebral body (black arrows) is the upper limit of normal intestinal diameter for clinical use.2 A small intestine:L5 ratio that is >1.6:1 and/or a mixed bowel population (some normal, some distended segments) may indicate obstruction.

In cats, normal small intestinal diameter (between white arrows) is considered ≤1.2 cm from serosal to serosal surface.7

Sagittal ultrasound image of a canine duodenum (between arrows). The small intestine is usually empty or contains minimal fluid and/or gas (*). Bowel-wall layers are readily identified with the hypoechoic mucosal layer (M) being thickest, surrounded by thin submucosal (hyperechoic), muscularis (hypoechoic), and serosal (hyperechoic) layers. Transverse images of small intestine are present in the near field.
2. Foreign Body Small Intestinal Obstructions

A foreign body (ie, rock) is identifiable in this canine small intestine. The markedly dilated segment of jejunum (arrows) leading up to the foreign body (~4× the height of L5) is significant.

Markedly gas-distended segment of jejunum (arrows) measuring ~2.2 cm in diameter is present ventral to the feces-filled colon (C) in this cat. The foreign body (arrow) appears as an abnormal, rectangular, heterogeneous radiolucent (gas) structure. Note the presence of normal bowel.

A longitudinal segment of severely fluid-distended small intestine (arrows) adjacent to normal bowel seen in transverse sections (*), suggesting obstruction. The greatly dilated lumen (L) shows speckled, echogenic fluid with readily observable movement in real-time examination. Potential cause (eg, foreign material, mass, intussusception) should be investigated. (K = caudal pole of kidney)

Small intestinal foreign material recognized as heterogeneous soft tissue opacity (arrows). Nearly all the small intestine is abnormally distended, indicating a distal small intestinal obstruction. The colon is empty. Distal small intestinal obstructions caused by radiographically nonopaque material warrants consideration of diffuse functional ileus. Differentiation between mechanical and functional small bowel dilation (eg, parvovirus infection, mesenteric torsion) can be difficult.

Ultrasound of small intestinal foreign material typically appears hyperechoic (small arrows) with strongly distal acoustic shadowing (large arrows), although this can vary depending on composition, shape, and number. Foreign material will not change shape with peristalsis and often has an organized surface for differentiation from intraluminal gas, which typically causes reverberation artifacts (ie, comet tails).
3. Inconclusive Radiographs and Definitive Ultrasound Images
Masses associated with small intestine may result in mechanical obstruction with typical signs of bowel dilation and abnormal luminal content. A mass not apparent on radiography may be diagnosed using ultrasonography.

Lateral abdominal radiograph of a dog with small intestinal obstruction. There is marked segmental small intestinal dilation (arrows) with heterogeneous soft tissue and mineral opaque material in the lumen. The cause (ie, the mass) is not identifiable radiographically; there is a large amount of normal empty small intestine.

Focal loss of wall layering and eccentric thickening of the intestinal wall (arrows) are present on ultrasound image showing abnormally dilated small intestinal lumen (L) orad to the mass. Normal empty small intestinal segments are seen in the transverse section in the near field (*). Surgery confirmed diagnosis of mucinous adenocarcinoma.
4. Intussusception Causing Small Bowel Obstruction

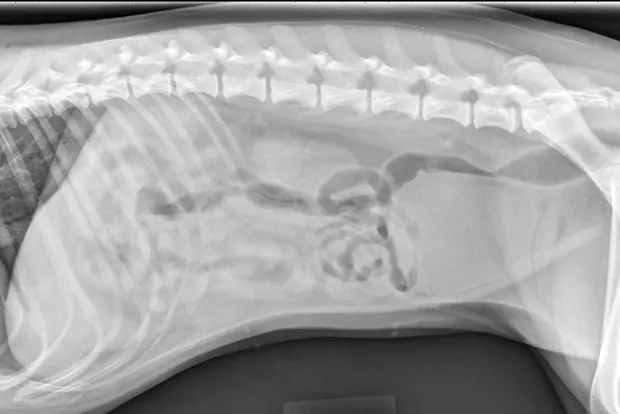
Marked diffuse small intestinal dilation (arrows). (C = colon)


Invagination of 1 portion of the GI tract (intussusceptum) into the lumen of another (intussuscipiens); this is often referred to as the target sign when seen in the transverse plane because of the multiple layers of adjacent intestinal walls.
5. Linear Foreign Body Obstructions
Linear foreign material often causes small bowel bunching, plication, or corrugation with or without severe intestinal dilation. String foreign bodies, more common in cats, can cause plication and/or corrugation, often without severe dilation. In dogs, cloth foreign bodies are more common and obstruction is often severe.


Lateral (Figure 5A) and ventrodorsal (Figure 5B) abdominal radiographs of a cat with string foreign body. Note the plicated (ie, ribbon candy) shape of small intestinal segments, bunched centrally. Pockets of triangular and odd-shaped abnormal intraluminal gas are present, common with linear foreign bodies.

To differentiate normal centralized small intestine from pathologic intestinal bunching, a plastic or wooden spoon may be used to place pressure on the lateral abdomen to disperse the intestinal segments. This cat demonstrated corrugation (ie, undulating serosal margins) of a segment of small intestine, seen in some cases of linear foreign body ingestion causing intestinal plication.

Intestinal plication (arrows) may be seen via ultrasound; in some cases, linear foreign material (arrowheads) may be visible within the small intestinal lumen.
6. Differentiating Small Intestine from Colon
This older cat presented for vomiting; ultrasonography was the first diagnostic modality.

Ultrasound image of an enlarged intestine (arrows) showing large amount of reverberation artifact (arrowheads) caused by luminal gas. This prohibits visualization of the far wall of this loop of bowel. The ultrasound impression was a distended colon.


Lateral (Figure 6B) and ventrodorsal (Figure 6C) abdominal radiographs of severely distended segment of bowel identified sonographically and properly diagnosed as severe small intestinal obstruction (arrows). Of note, there is fecal-like material in the small intestine. An ileocecocolic mass was diagnosed during exploratory laparotomy. This mass was apparently obscured by gas during ultrasound examination. (C = colon)