Image Quiz: Diagnosing Dermatophytosis in Dogs & Cats
Ashley E. Detwiler, DVM, DACVD, Pittsburgh Veterinary Dermatology, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
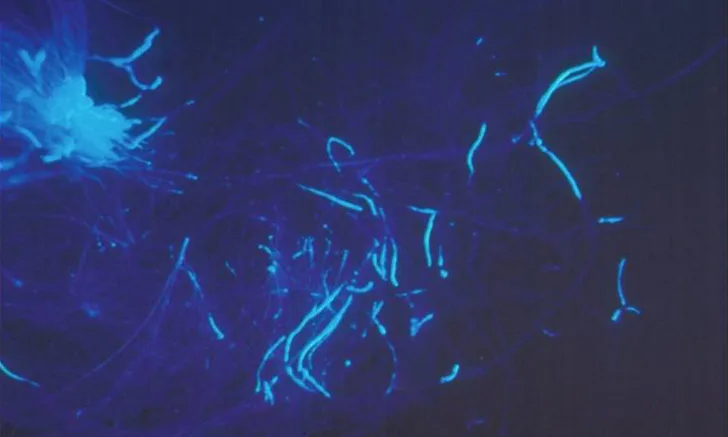
Dermatophytosis is a pathogenic, keratin-digesting, fungal infection of the hair, outermost layer of the skin (stratum corneum), and claw.1-5 Although uncommon, infection can also occur in the deep layer of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.1 In dogs and cats, dermatophytosis is most often caused by Microsporum canis, M gypseum, or Trichophyton mentagrophytes.1-5
All three organisms are zoonotic,1-5 with transmission most often linked to M canis (which also is zoophilic, as elaborated later). Of note, because M gypseum inhabits soil, it is zoonotic and geophilic1,4; whereas T mentagrophytes is found on rodents or in their environment, making this organism also zoophilic.1,4
Dermatophytosis is acquired following contact with
Infected hair or scale from animals
Fomites
Spores residing in soil
Spores in other outdoor or indoor environments
Individuals at increased risk of infection include1
Young
Geriatric
Immunocompromised
In Persian cats and Yorkshire terriers, genetics also may be involved, as both breeds commonly have repeat infections or difficulty clearing infections.1,2
The preference of M canis for an animal host makes this organism a zoophilic dermatophyte1,4; it also is the most frequent cause of dermatophyte infection in small animals and can be carried by asymptomatic cats.1,5 M canis infection is particularly important to avoid in catteries, shelters, and multipet environments or households.2,4,6
Clinical Presentation
Dermatophytosis can be focal or generalized1,3 affecting
Face
Ears
Legs
Tail
+/- trunk
Most patients have little to no evidence of pruritus, although chronic and extensive cases can be severely pruritic.
On skin, clinical presentation most often involves1-5
Partial to complete alopecia
Scale/dry or greasy seborrhea
Erythema
Papules
Pustules
Crusts
Epidermal collarettes (ringlike appearance)
+/- feline miliary dermatitis (crusted papules)
Nodules, draining tracts, feline chin acne, paronychia (inflammation of the claw fold), onychomycosis (fungal infection of the claw), or onychodystrophy (abnormal growth of the claw) occur less commonly.1-5
Global Relevance
Dermatophytosis occurs worldwide; however, prevalence of specific organisms varies by region.3,4 Because dermatophytosis is not a reportable disease, the overall incidence remains unknown.3 Dermatophytes grow best in warm, humid environments, including tropical and subtropical geographic areas.4 Risk for disease transmission increases with crowding, close contact, skin trauma, or contact with chronic moisture.3